Whatever your age, it is important to have your liver checked as part of regular health assessments. Most of all, ask your doctor for advice.

Since the development of liver disease, including fibrosis and steatosis, can be asymptomatic, the chances of early detection are increased during routine examination.
The diagnosis and follow-up of chronic liver disease is based on clinical examination. There are now many non-invasive examinations such as pulse elastography, and blood markers.
My Liver Exam sheds light on these different methods.
First, the clinical examination by your doctor
Clinical examination includes:
- First, assessment of your physical health.
- Abdominal palpation, to detect a possible liver disease (hard or bulky).
- And also percusion of the abdomen, the search for abnormal noises.1
- A diagnostic means (eg ultrasound, elastography, etc.) to evaluate the condition of the liver.
Biological examinations
These non-invasive biological tests should be prescribed and interpreted by your doctor as the results can be influenced by other elements such as inflammation.
During the interview with your doctor, he/she may prescribe a blood test to be performed in the laboratory. Once the results have been obtained, they will be sent to the doctor, who will decide whether further tests or even treatment are necessary.
For example, FibroMeter ™ is a non-invasive diagnostic test that evaluates the level of liver fibrosis from the determination of several biological parameters. It gives a score between 0 and 1 corresponding to the probability of significant fibrosis or cirrhosis with a single blood test.
Abdominal Ultrasound
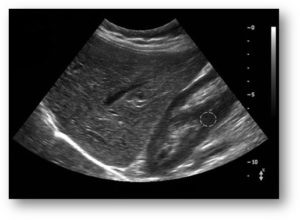
The purpose of this painless examination is to guide the diagnosis and detect any abnormalities. It is made with a non-irradiating ultrasound device. Remember that you must not eat nor drink 7 hours before the examination.2
It makes it possible to understand the makeup of the liver of liver tissues, which, in the case of steatosis, can appear particularly white in ultrasound. Still in case of steatosis, the liver increases in volume and has contours more or less distorted. Signs related to portal hypertension may be visible (venous dilation, collateral circulation).3
Hepatic biopsy
This examination consists in taking a fragment of the liver with a needle, in order to analyze it under a microscope. There are several types of biopsies. To find out more, do not hesitate to consult the Hepatobiliary Center Paul Brousse.
Nevertheless, this operation is invasive, it is not without drawbacks or even risks: painful in 20% of the subjects, it is complicated with haemorrhages in 0.1% of the cases and causes the death of 0.01% of patients.4 It cannot therefore be repeated easily. Moreover, it is subject to great variability from one operator to another, and this is an expensive examination.
Controlled vibration pulse elastography
Finally, FibroScan® ** technology (called VCTE ™: Impulse Elastography with Controlled Vibration) allows non-invasive measurement of liver elasticity, an efficient marker for the quality of liver tissue. The elasticity, in the physical sense of the term, corresponds to the ability of a substance to deform when a gentle mechanical hook is applied.
It is expressed in kilopascals (kPa) and increases with the hardness of the medium. The harder the liver, the more fibrosis is important.5
CAP ™ (Controlled Attenuation Parameter): paired with FibroScan® (VCTE ™), quantifies fatty liver disease. The entire exam takes less than 10 minutes.
Hence, we wanted to show you, through this article, the several possble examinations. Some are invasive, some are not. Remember that, if you are sensible to surgery operations, that non-invasive examinations are painless.
Legal mentions
* FibroMeter™ is classified as an in vitro diagnostic medical device and is manufactured by Echosens. The FibroMeter score is based on blood parameters and is indicated for the diagnosis and quantification of liver fibrosis in adult patients with chronic liver disease. It is expressly recommended to carefully read the guidance within the users’ guide together with the labeling of the device. Examinations must be performed according to the pre analytical and analytical recommendations from the manufacturer (www.fibrometer.com). Results obtained must be interpreted by a physician experienced in dealing with liver disease, taking into account the complete medical record of the patient.
**FibroScan® is a class IIa medical device according to Directive EC/93/42 and is manufactured by Echosens. Assessment of its conformity with the essential requirements of the Directive EC/93/42 is established by the LNE-G-MED (n°0459)- France – . FibroScan® is indicated for the non-invasive measurement of liver stiffness (E) and controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) in humans. It is expressly recommended to carefully read the guidance within the users’ guide and labeling of the device. FibroScan® examination must only be performed by operators certified by the manufacturer or its accredited local representative. The values obtained with FibroScan® must be interpreted by a physician experienced in dealing with liver disease, taking into account the complete medical record of the patient.
DISCLAIMER : These products are subject to regulatory requirements that vary from country to country and therefore may not be available for sale or distribution in all markets. This content is not intended for US audience : http://www.echosens.us/ .
References :
- http://www.vulgaris-medical.com/encyclopedie-medicale/examen-clinique
- http://www.gastroenterologue-paris-defense.fr/Qu-est-que-l-echographie-abdominale-Le-Dr-Costil-gastroenterologue-vous-informe-sur-cet-examen_25.html
- Aubé C, Winkfield B, Oberti F. New Doppler ultrasound signs improve the non-invasive diagnosis of cirrhosis or severe liver fibrosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;16:743-51
- CADRANEL JF, BARBARE JC. – Problèmes posés par la ponction biopsie hépatique en l’an 2000. Post-U 2000 (Journées Francophones de Nice) FMC-HGE : 41-43.
- http://asp-indus.secure-zone.net/v2/index.jsp?id=955/1232/3763&lng=fr

Dear sir,I have done fibroscan several times and had different scores each time .Two days ago idid the test three times and ihad the following scores ;the first one 8.8 the second 6.8 and the third 7.4 how do you explain this?
Hello,
My Liver Exam is here to provide you some information about your liver. We cannot replace your doctor. He/she is the only person that can interpret your FibroScan results. You should contact your doctor to talk to him/her about your FibroScan results.
Do not hesitate to contact us for more information.
Best regards.
My Liver Exam team
Very useful articles and I find it very supportive to understand the diagnosis of liver.